In the modern era with the rapid technological development in both fields of informatics and other sciences, new challenges have been reborn and with very specialized knowledge that need to be solved. In particular, with the spread of the pandemic around the world, it was expected to increase the use of the internet, connected digital devices, and digital technology in general. Combined with the pervasive and incalculable quantitative knowledge provided by the Internet, security issues have arisen and arise almost daily involving not only companies, organizations and government agencies, but even the simplest user.
Description Ransomware Virus
Ransomware virus is a form of malware that encrypts a victim’s files. The attacking user then demands ransom from the victim user to restore access to the data during payment. Victims are shown instructions on how to pay the ransom for obtaining the decryption key. Costs can range from a few hundred dollars to thousands, and cybercriminals usually require payment in Bitcoin. It is important to mention that they also use the dark or deep network.
There are several ways that Ransomware can use to access a terminal. One of the most common ways is phishing email, which contains attachments for the user victim and which are presented in disguise as files that the user must trust. Once these attachments are received and opened, they can take over the terminal. Some other more aggressive forms of ransomware take advantage of various security vulnerabilities to infect computers without having to deceive victims.
The choice of victims varies from case to case. Sometimes it’s a matter of opportunity. For example, a university may be the target because the number of people who make up the network security team is usually small and because there is a different user base that does a lot of file sharing. This data facilitates the intrusion into the system. In another case, some victims are more tempting goals because they seem more likely to pay the ransom quickly. For example, they often need medical facilities or government services access to their folders. Also, law firms and other organizations with sensitive data may be willing to pay to maintain their integrity, as they are particularly sensitive to leaks.
List of Latest Ransomware Attacks
Here are the most popular ransomware viruses that have occurred recently in the cybersecurity landscape
- Reyptson
- Leakerlocker
- Wysiwye
- Osiris
- Cerber
- Locky
- NotPetya
- Wannacry
- Cryptolocker
Ransomware Functions
The main functions of ransomware are based on cryptography for file encryption. It has been found that powerful cryptographic libraries are used, from the built-in Microsoft Crypto API, in specific language libraries from JavaScript and Python. With early variants of ransomware, it was the file itself that was encrypted, usually with a public RSA key. As is known with 32 public key encryption, the private key will be required for decryption, which will be held on the C2 server for ransomware. For example, when CryptoLocker appeared, it introduced a combination of cryptographic functions. Initially, it would generate a random symmetric key for each file, the contents then encrypted by the AES algorithm, followed by further encryption via public key RSA, 1024 and 2048 bits recorded as used. Modern iterations have added the Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman as a method of removing security professionals from the secret key.
Overall, the cryptographic algorithms used today do not differ much from RSA and AES, although the method of calling algorithms by Microsoft Crypto API is considered an easy detection method as presented by Kotov and Rajpal, so static links are incorporated into the program functions ransomware.
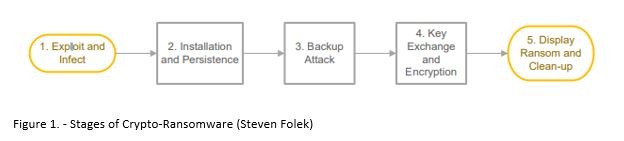
Approaches to Ransomware Analysis
Analysis of malware can be classified into two main categories: static analysis and dynamic analysis. Before performing any malware analysis, it is recommended to configure a dedicated environment which is isolated from other machines and network resources that are not to be considered within the scope of the analysis.




