A simple explanation for cloud computing would be not storing data, applications and information on local hard disk or local servers, but storing it away from our physical location. When we need all of them (data, applications, information), access is obtained via the Internet. Access to data and information is not confined to any location, and that is the essence of cloud computing.
Cloud computing is a model versatile technology for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction(NIST).
Essential Characteristics
Characteristics of Cloud Computing NIST specifies five characteristics of cloud.
♦ On-demand self-service: Computing capabilities can be provided to a customer according to the requirement of the user. Capabilities like storage and server time are allocated without human interaction.
♦ Broad Network access: Using standard mechanisms, the cloud can be accessed through network using thick or thin clients. Examples of the clients are tablets, laptops, mobile phones and workstations.
♦ Resource pooling: In the multitenant model, the computing resources are pooled to provide service to multiple consumers. The computing resources can be present anywhere geographically and the exact location of resources is not known to the user.
♦ Rapid Elasticity: Depending on the user requirement, the capabilities and resources in the cloud can be released and provided automatically.
♦ Measured Service: The services provided to the user are measured by the cloud system and are reported to the user and the provider. Based on the type of service, the cloud system optimizes and controls the resource use by a metering capability.
Different Types of Cloud
Clouds come in different types, depending on the requirements, policies, and essential characteristics. There are two primary deployment models of cloud: public and private. Most companies and organizations use a combination of private computing resources (data centers and private clouds) and public services, where some of the services existing in these environments interact with each other. This is the hybrid cloud environment as called. Also, many organizations use a variety of public cloud services to support different developer and business units. This is the multicloud environment as called.
Public Cloud
In simple terms, public cloud services are characterized as being available to clients from a third party service provider via the Internet. The term “public” does not always mean free, even though it can be free or fairly inexpensive to use. A public cloud does not mean that a user’s data is publicly visible; public cloud vendors typically provide an access control mechanism for their users. Public clouds provide an elastic, cost effective means to deploy solutions.
Private Cloud
A private cloud offers many of the benefits of a public cloud computing environment, such as being elastic and service based. The difference between a private cloud and a public cloud is that in a private cloud-based service, data and processes are managed within the organization without the restrictions of network bandwidth, security exposures and legal requirements that using public cloud services might entail.
Hybrid Cloud
As we mentioned hybrid cloud is a combination of a public and private cloud that interoperates. In this model users typically outsource non business-critical information and processing to the public cloud, while keeping business-critical services and data in their control.
Multicloud
Many business initially found that they had a multicloud environment because different development teams or business units were choosing to use varying public clouds. As we can imagine, as business found themselves using multiple clouds, finance, operations and IT teams needed a way to gain visibility, control, and choice between clouds.
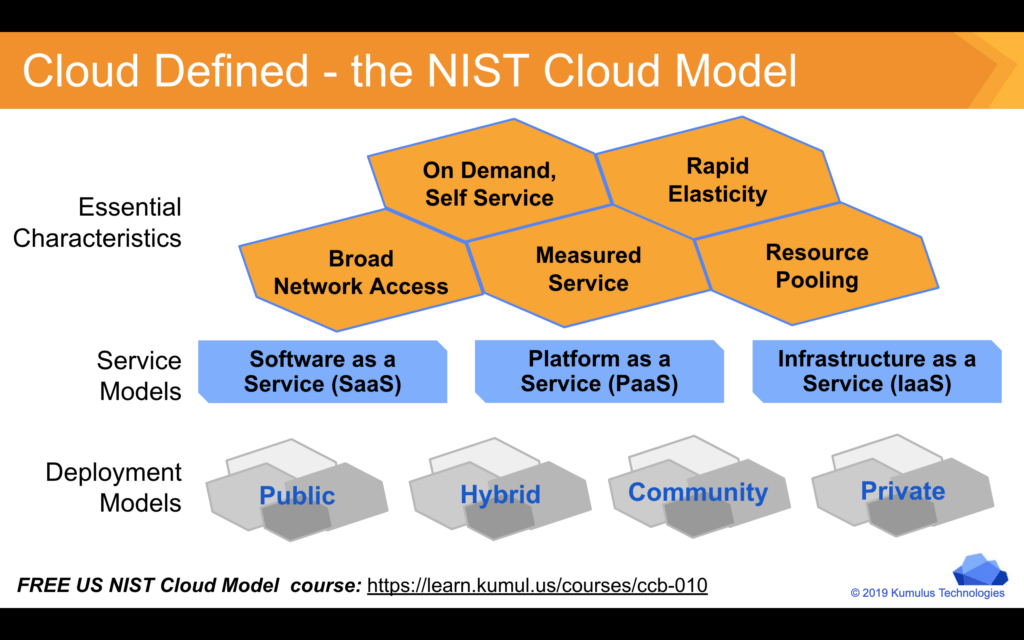
Service Models
The foundations of cloud computing calls for an understanding of cloud delivery models. The models that represent computing environments are:
· IAAS Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a service model (IaaS), the service provider provides basic computing abilities to the clients. The client gains control of the storage, networks, and other computing capabilities by renting the services from the provider. Though the customer has control over the storage system and operating system, they do not control the overall cloud infrastructure.
· PAAS Platform as a Service
In the platform as a service (PaaS), a development platform is offered as a service. The platform enables clients to build their applications that run on the service provider’s infrastructure
· SAAS Software as a Service
Software as a Service (SaaS) model, the client can access the provider’s infrastructure through an interface. Most commonly used interfaces are web browsers. In this model a single instance on the service provider’s end supports multiple access instants on the client’s side. One main advantage of this model is that the consumer does not incur software licensing cost.



